What is Corporate Performance Management?
Every company can benefit from a corporate performance management (CPM) strategy, but it’s especially useful for those that want to modernise their financial planning and make more data-driven decisions for maximum future performance.
Corporate performance management (CPM) refers to software systems that increase efficiencies and data accuracy in finance and accounting processes, enabling companies to measure and analyse their past performance to make better business decisions that maximise future performance—both in bottom line financials and operational KPIs.
Software systems that measure and analyse financial data in order to inform strategic decisions go by several names—including business performance management (BPM) and enterprise performance management (EPM)—but in general, these terms are synonymous with CPM.
New enhancements in cloud financial solutions have bridged the gap between applications that merely process and track transactions, and those that manage the full spectrum of financial planning and analysis (FP&A). CPM has merged with FP&A, allowing finance teams to not only monitor and manage their companies’ past and present performance, but also to plan for future performance improvements using insights and analysis from both financial and operational data.
What is CPM Software?
CPM software is a set of tools and processes that include reporting, planning, budgeting and analysis. An organisation’s CPM output is the first step towards facilitating revenue growth and managing expenses. As the industry pivots from CPM to incorporating FP&A practices into every area of the business, the associated software has evolved as well. Modern FP&A software incorporates these key CPM functions, providing more power and more opportunity to organisations that embrace full-spectrum FP&A.
Traditionally, CPM software has been segmented into:
- Financial CPM: accounting processes, namely financial close management including closing the books, consolidations, account reconciliations and preparation of financial statements/financial reporting
- Strategic CPM: finance processes, namely budgeting, planning and forecasting, i.e., the traditional definition of FP&A
Until recently, these were typically sold to different audiences with different value propositions:
- Accounting (Financial CPM): increase efficiency of close process and accuracy of financial statements and reporting
- Finance (Strategic CPM): increase budgeting, forecasting accuracy and efficiency, and elevate the strategic role of finance in business-wide planning
The evolution from segmentation to “full-spectrum” FP&A is due to the fact that the two sides of CPM are symbiotic: modern finance leaders should look at FP&A as an all-encompassing term for measuring, managing and reporting on their company’s past, present and future performance. Actuals from accounting need to feed into budgets, forecasts and analysis to inform better business decisions for the best future performance possible.
The key differentiator between traditional CPM and full-spectrum FP&A is integrated business planning. Modern FP&A solutions and processes combine financial and non-financial data and KPIs to inform better departmental and business-wide decisions for the best future performance. Here’s a look at each of the key areas of performance management—what they are and how they’ve evolved.
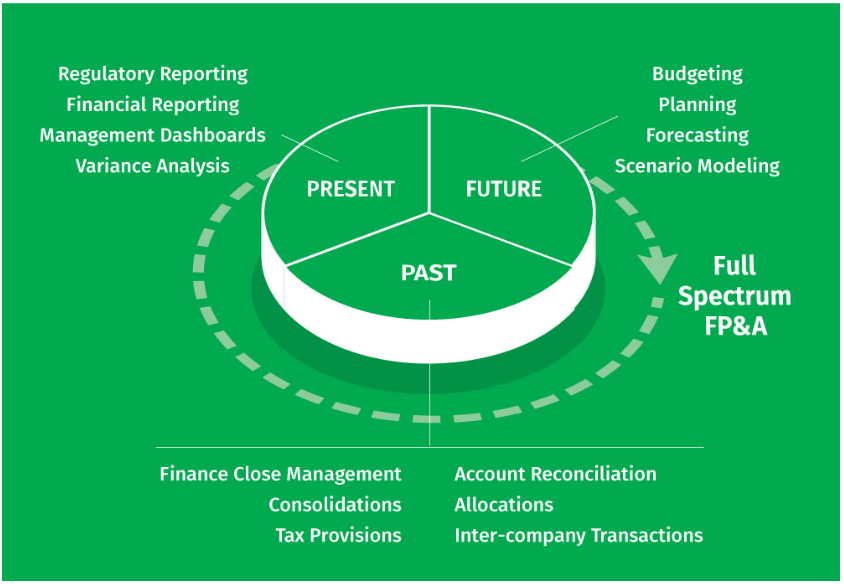
CPM and FP&A by Process
Financial Close and Consolidation
- Definition: The financial close and consolidation process provides actual numbers for organisations to analyse against planned numbers.
- Full-spectrum solution: Modern software automates the financial close process—this means having to enter less data manually, which results in increased accuracy and more time for analysis. FP&A solutions also carry out a streamlined and automated consolidation process with in-depth audit logs and operations-based workflow.
Reporting
- Definition: Reports include cash flow, income statements, balance sheets and other important business metrics, as well as regulatory reports like CCAR and 10Ks.
- Full-spectrum solution: Software enables self-serve reporting, so businesses can build summary reports with easily accessible details using a familiar Excel interface, without help from IT or a vendor consultant.
Budgeting, Planning and Forecasting
- Definition: Planning outlines a company’s course of financial direction, while budgeting records how the plan will be followed each month. Budgeting also includes debt reduction, cash flow and revenue estimates. Forecasting uses market conditions, business drivers and historical data to predict a company’s financial outcome in the upcoming days/weeks/months and years.
- Full-spectrum solution: Full-spectrum software combines financial and non-financial data to inform management on the best business-wide planning decisions—budgets may be financial, but plans are cross-departmental. Modern software solutions also allow teams to implement a rolling forecast model of regularly updated forecasts, which leads to continuous improvement and increased forecasting accuracy with every iteration.
Modelling and Analysis
- Definition: Modelling uses data to create projected scenarios of how financial processes may be affected by various market and internal events, and analysis is the process of evaluating the data that comes from these models.
- Full-spectrum solution: Modern software solutions use information from multiple sources such as accounting, business operations and finance to test models that predict how operational decisions might affect a company’s financial future.
CPM and Excel
While ERP modules and specialised CPM software abound, Excel still remains the most popular software tool for performing CPM, and it makes sense—it’s intuitive, familiar and everywhere in business, especially in finance and accounting departments. It’s only natural that Excel is the software users gravitate towards for any financial analysis or reporting need.
Excel is built with flexibility at the forefront, so users don’t need help from IT consultants to build budget reports or perform data analysis. At the same time, it has a powerful interface that includes hundreds of functions for data visualisation and statistical analysis.
Finance and accounting professionals have relied on Excel for their entire careers, and it remains a highly-sought skill among candidates. Plus, countless companies have invested in training employees and building customized Excel models, templates and report formats. In fact, Excel is so popular that if it was a language, it would be one of the world’s largest, with nearly a billion speakers.
To Excel or Not to Excel
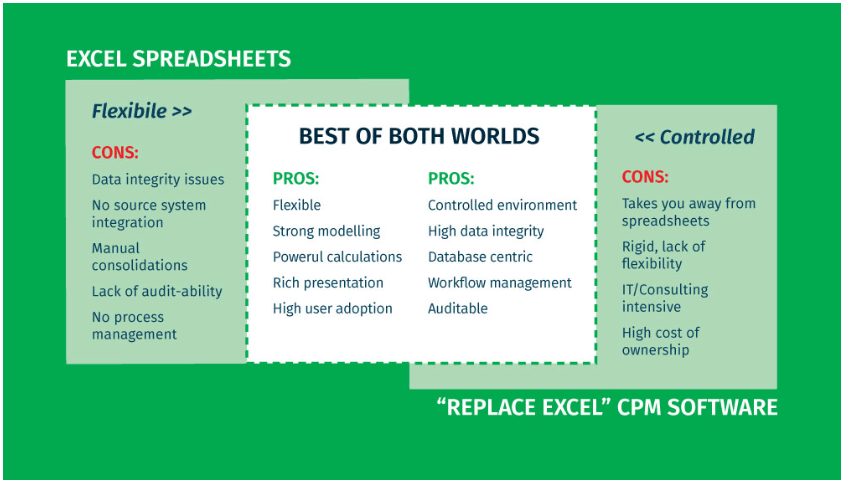
Organisations rely on Excel for its power, flexibility, and because they know it inside and out. But it’s not perfect. Weaknesses include a lack of:
- Underlying database
- Integration with company-wide databases and software
- Version control, audit trail, permissions, and other security controls
- Workflow automation
- Anytime, anywhere, any device access
- Drill-down reports
- Status tracking
- User-level permissions
Excel Imitators
Many CPM software vendors are convincing their customers to abandon Excel-based approaches in favor of their proprietary emulations. These solutions are similar to Excel, but lack its flexibility and power, and require a long, continual and costly process of customisations to make the software fit the company’s unique needs.
What’s more, 84 percent of companies that buy proprietary CPM software to replace Excel end up exporting their data back to Excel anyway. Why? Because accounting and finance professionals prefer its flexibility and familiarity.
But exporting back to Excel defeats the purpose of a secure, controlled program in the first place. It also perpetuates the problem of “shadow systems,” additional software being used outside of company-approved solutions. In this scenario, you’re back at square one—facing the same challenges as using Excel on its own.
Integration: The Best of Both Worlds
The solution to this dilemma? Integrate advanced features with Excel’s flexible interface. By combining Excel’s familiar interface—not just emulating the look and feel, but real, actual Excel—with a cloud-based solution, organisations can fix inefficiencies without compromising the power of a tool they’re already familiar with.
Excel integration is more than just deploying an “Excel-like” solution—integration combines the powerful functions of the original software with the benefits of a modern, scalable cloud solution.
The Future of CPM
BPM Partners’ Next Generation of CPM report explains that the next generation of performance management solutions will have four core characteristics:
- Comprehensive: A comprehensive program will go beyond the office of finance to deliver a holistic viewpoint of an organisation. It allows senior management to understand the effects of new decisions on different parts of an organisation.
- Connected: When the number of CPM software users in each department grows, there’s a need for more systems to be connected. This way, finance departments can get the bigger picture: operational trends, market changes, sales and product development—not just revenue.
- Collaborative: Innovative CPM designs will make it easier for users to share reports and data, turning business planning into a collaborative process. Executive management can share data and reports to move ahead with different goals.
- Cloud: Cloud-based CPM solutions can enhance scalability and accessibility while providing better security than on-site software.
Focus on Usability
In addition to the four characteristics above, advanced CPM applications must focus on providing usability—not only to finance professionals, but especially to users without a finance background. In order for enterprise software to realize its value, it must be adopted by employees. Ease of use, or “employee-centered” design, is the first step toward better performance: The value chain for an optimal CPM solution starts with increased usability.
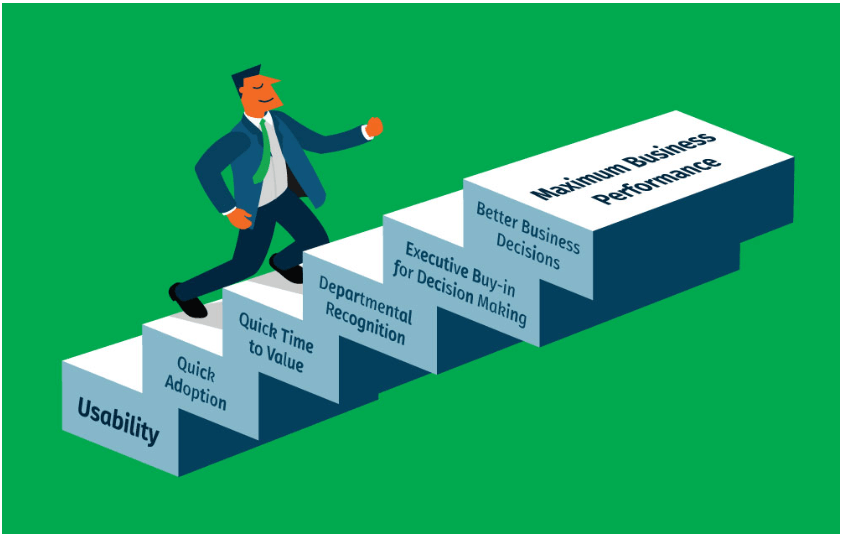
Usability leads to quick adoption, and quicker adoption means the finance departments can see quicker time-to-value. By getting everyone on board more efficiently and generating ROI earlier, word’s going to spread—and that means more recognition for the department who led the charge, easier buy-in from decision makers, and, ultimately, better decisions and business performance.
“CPM isn’t just for accountants anymore. We’re seeing broader use throughout organizations which in turn is leading to greater adoption rates. This is making usability an important factor in current and future development trends. The end goal here is to achieve greater efficiency with analytics integration, more effectively empowering end-users.”
Full-Spectrum FP&A
Full-spectrum FP&A software incorporates all the competencies of CPM to deliver a diverse spectrum of effective features. From financial close and scenario modelling to improving planning strategies for future business performance, FP&A solutions deliver reliable data and instant access to forecasted numbers.
With a user-friendly cloud-based FP&A solution, finance teams don’t need to rely on vendors or IT consultants to get the most out of their software—they’ve got self-serve dashboards and drill-down reports to quickly get the information they need, and share it with others across the organization.
Full-spectrum FP&A is the logical next step of CPM, giving finance teams clarity and confidence in their numbers with a centralised single source of truth, with automation that frees up time for analysis. Executives and members of senior management can make better decisions when they have real-time data at their fingertips—and that’s better for everyone.
Looking to get started with Vena’s ground-breaking FP&A solution? Speak to a consultant at Vena’s U.K. partner Influential Software.
